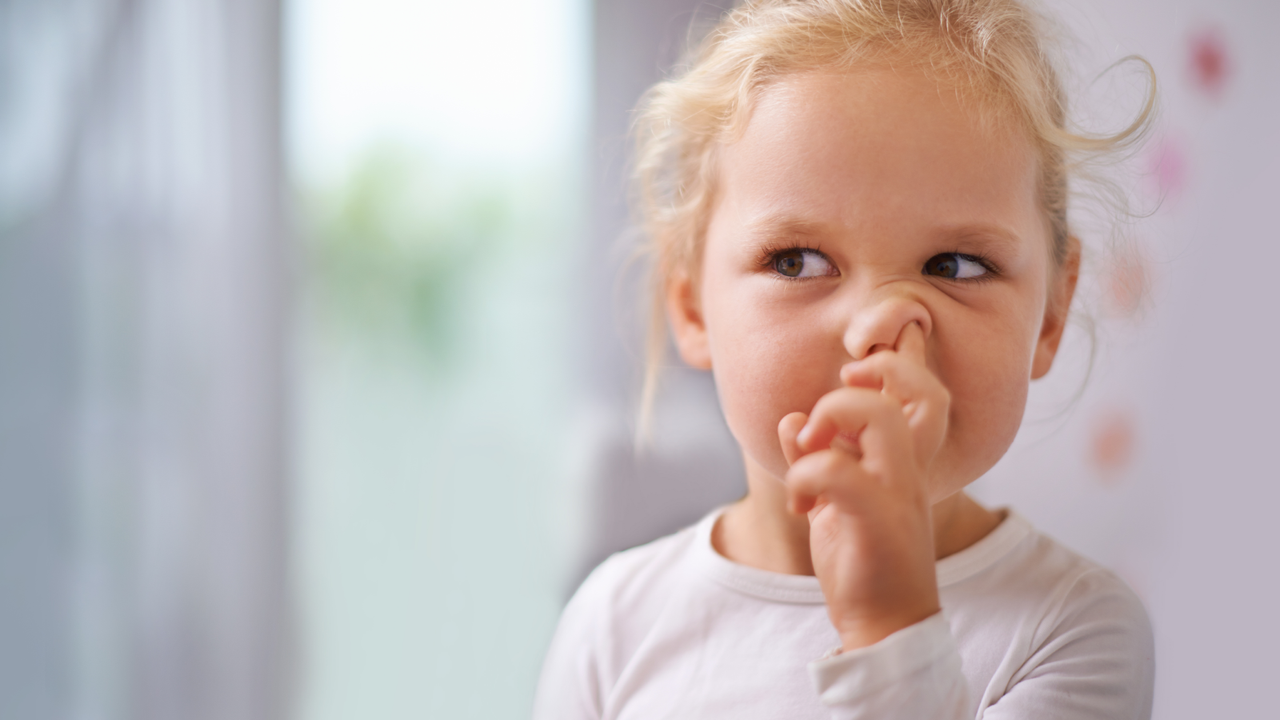
- Human Behavior
 Why do kids eat their boogers?
Features
By
Emma Bryce
published
7 February 2026
Why do kids eat their boogers?
Features
By
Emma Bryce
published
7 February 2026
There may be something more than just a bad habit behind this behavior.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.
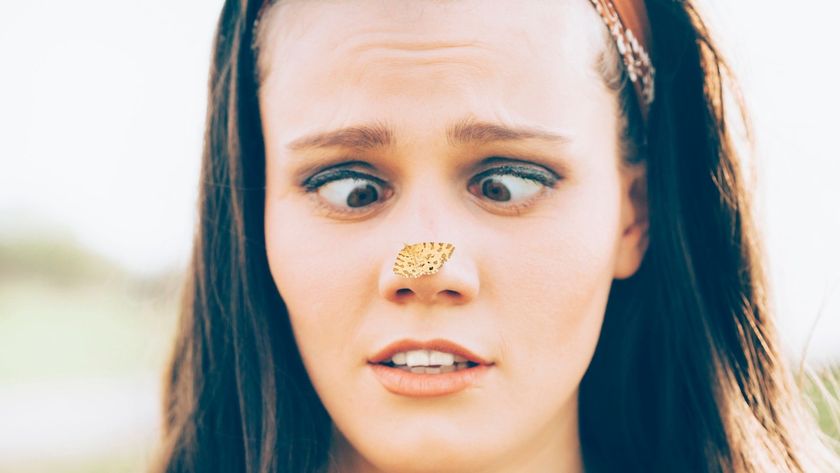
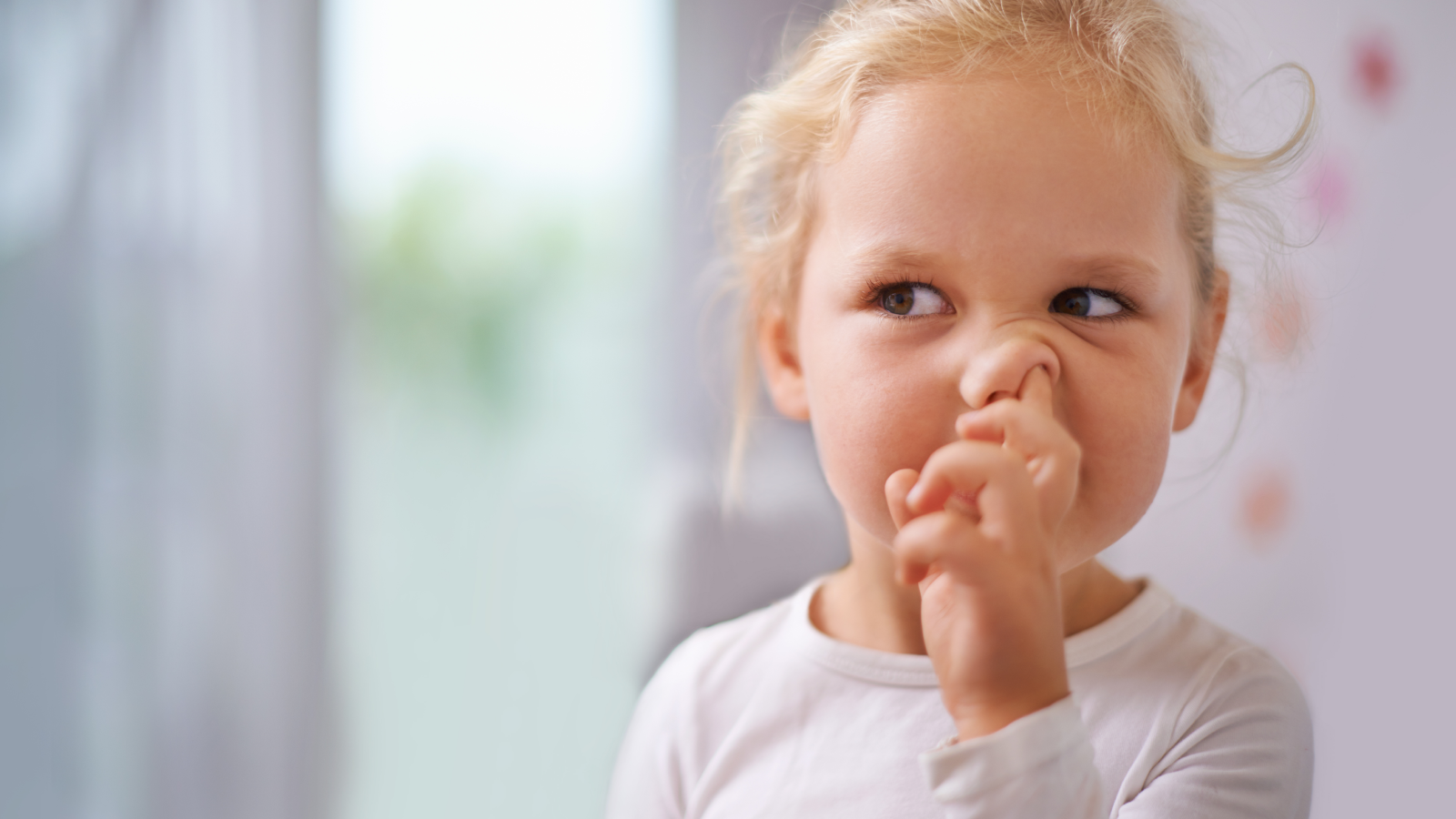 Kids, adults and other primates like chimpanzees are known to pick their noses and eat their boogers.
(Image credit: PeopleImages/Getty Images)
Kids, adults and other primates like chimpanzees are known to pick their noses and eat their boogers.
(Image credit: PeopleImages/Getty Images)
- Copy link
- X
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Become a Member in Seconds
Unlock instant access to exclusive member features.
Contact me with news and offers from other Future brands Receive email from us on behalf of our trusted partners or sponsors By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.
Signup +
Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.
Signup +
Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more
Signup +
Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Signup +
Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.
Signup +
Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Signup +Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Explore An account already exists for this email address, please log in. Subscribe to our newsletterWe've all seen it: a kid with one finger wedged up a nostril, mining the cavity for a golden nugget, teasing it out, and then gobbling it like a tasty snack. It may be gross to adults, but most children seem completely unfazed. So why do kids eat their boogers, and are they possibly onto something?
Most parents will tell you how common it is for children to eat their own mucus — a behavior known as "mucophagy" — yet data on its prevalence are scarce.
You may like-
 'Nose-in-a-dish' reveals why the common cold hits some people hard, while others recover easily
'Nose-in-a-dish' reveals why the common cold hits some people hard, while others recover easily
-
 50 mind-blowing science facts about our incredible world
50 mind-blowing science facts about our incredible world
-
 Why don't you usually see your nose?
Why don't you usually see your nose?
However, researchers have found that mucophagy is shared by at least 12 other primate species.
Evolutionary biologist Anne-Claire Fabre first discovered this when watching the aye-aye (Daubentonia madagascariensis). This lemur species is known for its 3-inch-long (8 centimeters) middle finger, which it uses to pry insects out of hard-to-reach crevices. But when Fabre was watching a captive aye-aye in 2015, she was surprised to see it sticking that long, thin digit into its nostrils; extracting mucus; and then licking its finger clean.
Sign up for our newsletter

Sign up for our weekly Life's Little Mysteries newsletter to get the latest mysteries before they appear online.
"It was hilarious and disgusting at the same time," recalled Fabre, an associate professor at the University of Bern in Switzerland. "It seemed that it was really enjoying what it was doing. It's something that they do pretty often." (It's possible that the captive aye-aye was unusual in its nose-picking habit, but there's no reason to assume this doesn't also happen in wild aye-ayes, Fabre said.)
This made Fabre wonder if other primates eat their mucus, too. When she carried out a literature review that included her own observations of the aye-aye, she found evidence that gorillas, bonobos, chimpanzees, macaques, capuchins and other primates also pick their noses and eat the mucus. Most species used their fingers, but some used sticks to pry out the spoils. Some primates even extended the favor, picking others' noses too, the research found.
"When you see the composition of mucus, it's mostly water, at more than 98%," Fabre said. The remainder is composed of a protein-carbohydrate ingredient called mucins, and salts. It's possible that animals reap some benefit from consuming these ingredients, the way that some species will eat their own feces to digest the remaining nutrients there, Fabre explained.
This idea raises the question of whether there may be a deeper evolutionary basis for mucophagy in humans.
Mucus creates a protective layer that traps dust, spores and disease-causing microorganisms as we inhale, before it reaches the lungs. In 2013, a biochemist shared a hypothesis that eating boogers could therefore expose children to small doses of pathogens that train the immune system to identify these molecules and can help to trigger an immune response. However, this idea was not ultimately tested in empirical research.
You may like-
 'Nose-in-a-dish' reveals why the common cold hits some people hard, while others recover easily
'Nose-in-a-dish' reveals why the common cold hits some people hard, while others recover easily
-
 50 mind-blowing science facts about our incredible world
50 mind-blowing science facts about our incredible world
-
 Why don't you usually see your nose?
Why don't you usually see your nose?
Dr. Chittaranjan Andrade, author of the 2001 nose-picking study in teenagers, is wary about such theories. "I am skeptical. Any immune substance that survives drying in the mucus is likely to be very small in quantity, and it is also likely to be digested after ingestion," therefore likely having a limited effect, the senior professor emeritus at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences in Bangalore, India, explained in an email.
Other experts have cautioned that because nasal mucus can spread pneumonia-causing bacteria, nose picking and mucophagy in children should be controlled when they are around immunocompromised people.
With no evidence behind the idea that mucophagy boosts immunity, researchers have looked for more intuitive reasons why kids eat their own mucus. Boogers can create itching, tightness, and discomfort in the nose that might prompt nose-picking, and curious children might then give it a taste-test, Fabre suspects.
One researcher asked children directly why they ate their boogers. The results were published in a 2009 book chapter that was not peer-reviewed and were based on a very small sample of just 10 children. But their insights included the fact that they liked eating boogers simply because of their appealing texture and taste.
RELATED STORIES—Why does water squirt out of your eye if you blow your nose really hard?
—Does coffee really stunt kids' growth?
—How accurate are our first childhood memories?
Andrade believes that children develop this habit because it doesn't yet have the negative association that it carries for older people. "Because [children] do it openly, they are observed and scolded, and because the act, picking as well as eating, is stigmatized, my guess is that they do not repeat it, not openly anyway," Andrade said.
Until there's concrete research into the question, the answer to precisely why children eat their boogers will remain elusive. To Fabre at least, it's a topic that deserves more investigation to understand if there are possible benefits or harms of mucophagy to child development.
Ultimately, she takes kids at their word and believes that they may eat their boogers simply because they like it. "It's something that is crunchy and a little bit salty," she says. And having watched nose-picking aye-ayes for hours and learned about the prevalence of this habit in other species, it no longer gives Fabre the ick: "Honestly, in my opinion, it's not something that is disgusting."
TOPICS Life's Little Mysteries children Emma BryceLive Science Contributor
Emma BryceLive Science ContributorEmma Bryce is a London-based freelance journalist who writes primarily about the environment, conservation and climate change. She has written for The Guardian, Wired Magazine, TED Ed, Anthropocene, China Dialogue, and Yale e360 among others, and has masters degree in science, health, and environmental reporting from New York University. Emma has been awarded reporting grants from the European Journalism Centre, and in 2016 received an International Reporting Project fellowship to attend the COP22 climate conference in Morocco.
View MoreYou must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
Logout Read more 'Nose-in-a-dish' reveals why the common cold hits some people hard, while others recover easily
'Nose-in-a-dish' reveals why the common cold hits some people hard, while others recover easily
 50 mind-blowing science facts about our incredible world
50 mind-blowing science facts about our incredible world
 Why don't you usually see your nose?
Why don't you usually see your nose?
 What causes the feeling of 'butterflies' in your stomach?
What causes the feeling of 'butterflies' in your stomach?
 'Perfectly preserved' Neanderthal skull bones suggest their noses didn't evolve to warm air
'Perfectly preserved' Neanderthal skull bones suggest their noses didn't evolve to warm air
 Remnants of spills on Renaissance-era textbook reveal recipes for 'curing' ailments with lizard heads and human feces
Latest in Human Behavior
Remnants of spills on Renaissance-era textbook reveal recipes for 'curing' ailments with lizard heads and human feces
Latest in Human Behavior
 Daily sudoku: Take a break with this classic numbers puzzle
Daily sudoku: Take a break with this classic numbers puzzle
 Live Science crossword puzzle #28: Largest desert in Asia — 6 across
Live Science crossword puzzle #28: Largest desert in Asia — 6 across
 Live Science crossword puzzle #27: The explosion that created the universe — 5 down
Live Science crossword puzzle #27: The explosion that created the universe — 5 down
 Live Science crossword puzzle #26: Nothing can travel faster than this — 12 across
Live Science crossword puzzle #26: Nothing can travel faster than this — 12 across
 Live Science crossword puzzle #25: Ancient hominin species famous for their 'upright' posture — 11 across
Live Science crossword puzzle #25: Ancient hominin species famous for their 'upright' posture — 11 across
 Live Science crossword puzzle #24: Elemental particle associated with light — 11 down
Latest in Features
Live Science crossword puzzle #24: Elemental particle associated with light — 11 down
Latest in Features
 Bandera Volcano Ice Cave: The weird lava tube in New Mexico whose temperature is always below freezing
Bandera Volcano Ice Cave: The weird lava tube in New Mexico whose temperature is always below freezing
 Psychedelics may rewire the brain to treat PTSD. Scientists are finally beginning to understand how.
Psychedelics may rewire the brain to treat PTSD. Scientists are finally beginning to understand how.
 Why do kids eat their boogers?
Why do kids eat their boogers?
 Trippy 'biomass' snap reveals first detailed look at our planet's carbon stores
Trippy 'biomass' snap reveals first detailed look at our planet's carbon stores
 When were boats invented?
When were boats invented?
 Psychedelic drug ayahuasca could treat PTSD, early studies hint. But exactly how it works isn't clear.
LATEST ARTICLES
Psychedelic drug ayahuasca could treat PTSD, early studies hint. But exactly how it works isn't clear.
LATEST ARTICLES 1'Invisible scaffolding of the universe' revealed in ambitious new James Webb telescope images
1'Invisible scaffolding of the universe' revealed in ambitious new James Webb telescope images- 2Extraordinary photo captures first appearance of Siberian peregrine falcon in Australia's arid center
- 3Scientist accidentally stumbles across bizarre ancient ‘wrinkle structures’ in Morocco that shouldn't be there
- 4Psychedelic drug ayahuasca could treat PTSD, early studies hint. But exactly how it works isn't clear.
- 5Psychedelics may rewire the brain to treat PTSD. Scientists are finally beginning to understand how.



