- Space
- Astronomy
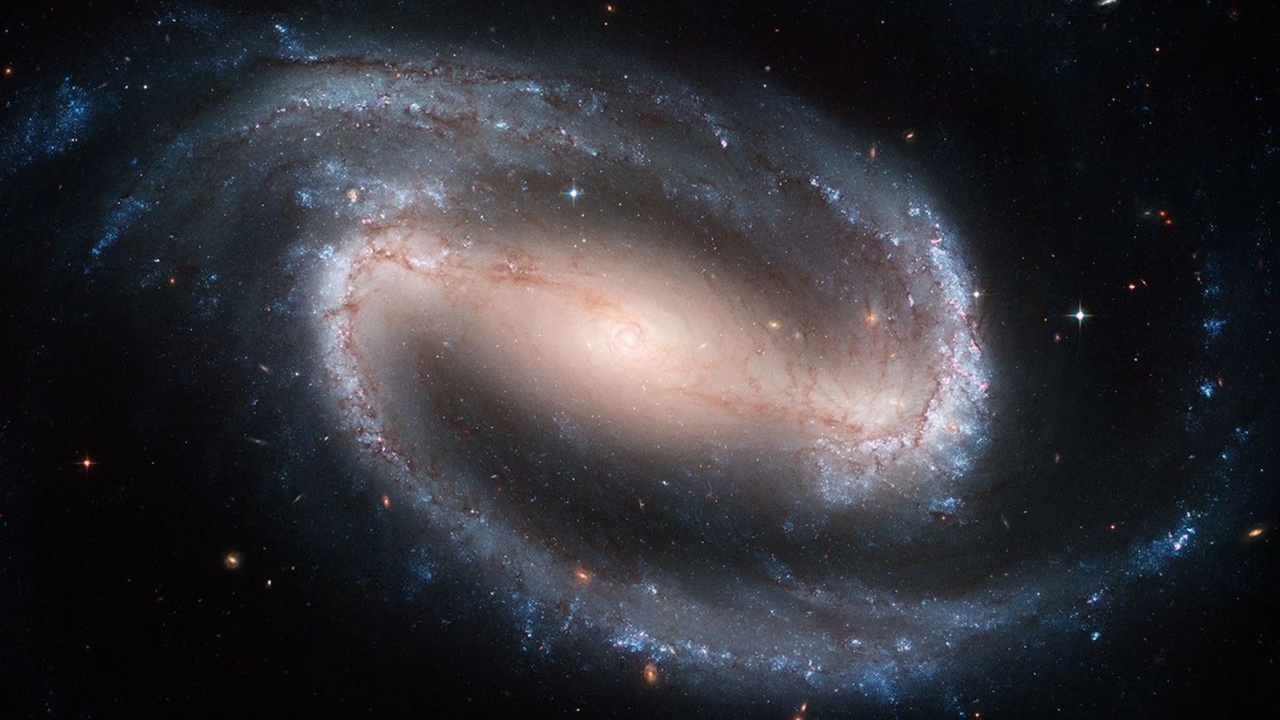
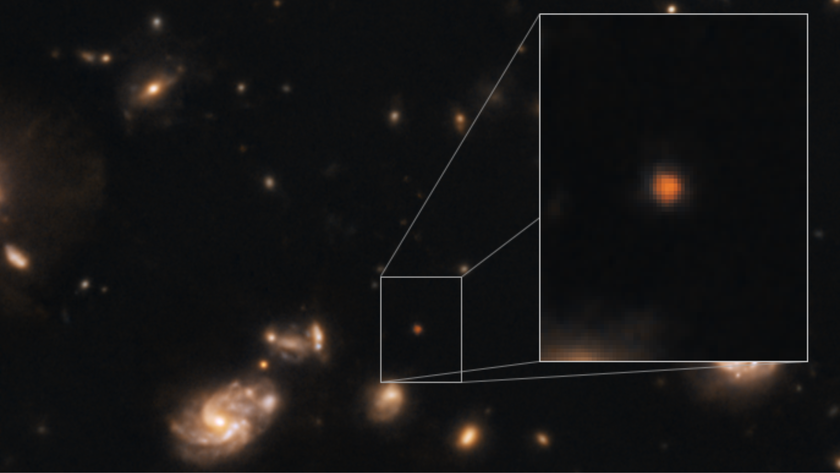
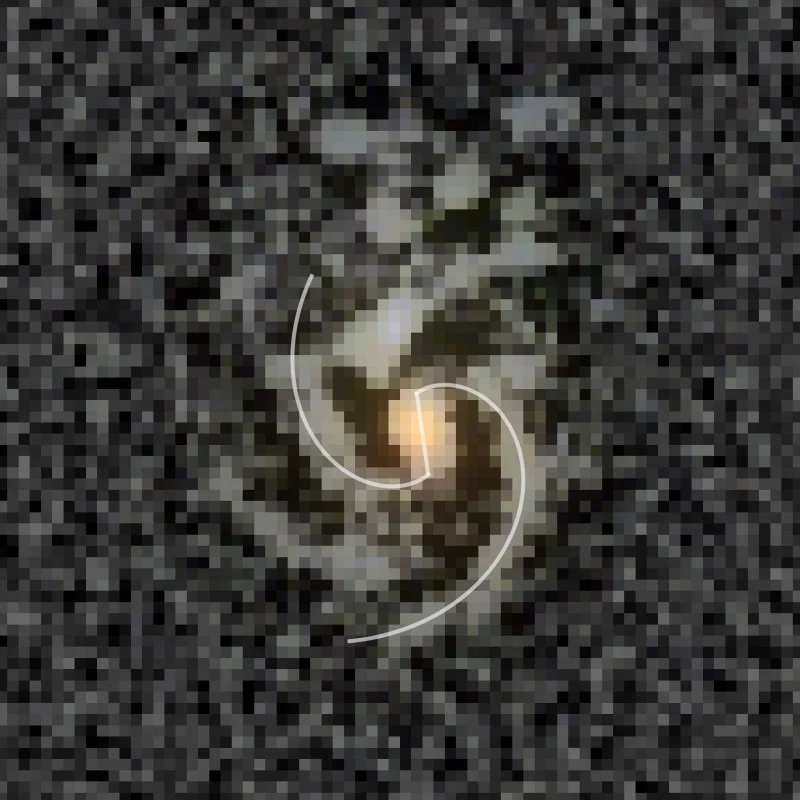
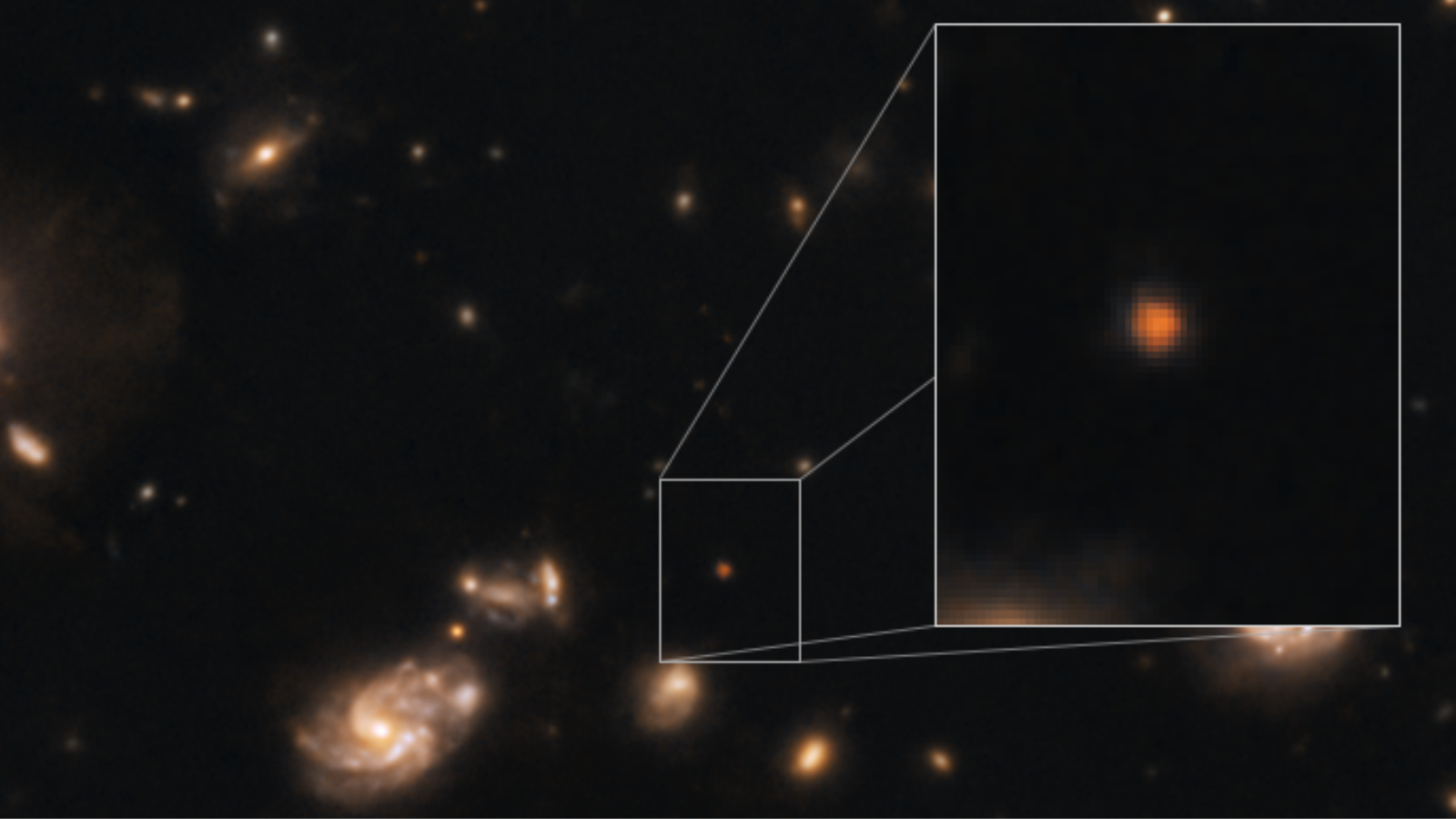
Astronomers have confirmed the earliest barred spiral galaxy in the universe, a Milky-Way-like structure that existed just 2 billion years after the Big Bang.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.
 (Image credit: Ivanov, D. et al. (2026))
Share
Share by:
(Image credit: Ivanov, D. et al. (2026))
Share
Share by:
- Copy link
- X
Scientists continue to push the boundaries of astronomy and cosmology, thanks to next-generation instruments that can see farther and clearer than ever before.
Through these efforts, astronomers have observed some of the earliest galaxies in the Universe. In turn, this has led to refined theories and timelines of galactic formation and evolution.
You may like-
 James Webb telescope may have discovered the earliest, most distant black hole ever seen
James Webb telescope may have discovered the earliest, most distant black hole ever seen
-
 James Webb telescope may have spotted the earliest supernova in the universe
James Webb telescope may have spotted the earliest supernova in the universe
-
 'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
According to the Hubble Sequence, galaxies are grouped into elliptical, spiral, and lenticular based on their morphological characteristics. Whereas galaxies generally begin as irregular disks, they evolve to form spiral arms extending from a central bulge (aka. a spiral galaxy).
Barred spirals, such as the Milky Way, also have a bar-shaped linear arrangement of stars across their centers, which play an important role in their evolution by funneling gas inward from the outer reaches, feeding the supermassive black hole in the center, and suppressing star formation throughout the stellar disk.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter nowContact me with news and offers from other Future brandsReceive email from us on behalf of our trusted partners or sponsorsBy submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.

—'Mind-blowing' James Webb telescope images reveal 19 spiral galaxies in the greatest detail ever seen
—Bizarre 1-armed spiral galaxy stuns Hubble scientists
—The tilted spiral galaxy that took Hubble 23 years to capture
While researchers have reported barred spiral galaxies that are even older, analyses of these candidates have been less conclusive, as the observations were made using gravitational lensing or redshift measurements. Whereas the former method is hampered by the lensing effect, which often blurs the light from the more distant object, redshift measurements are subject to errors and uncertainties of 10-15%. Neither method is as definitive as spectroscopy, which was used to validate the age of COSMOS-74706.
The discovery of a barred spiral galaxy this early in the Universe was not entirely surprising, as some simulations suggest that bars were forming in galaxies as far back as 12.5 billion years. However, observational evidence of such structures has been much harder to come by, making this a significant discovery that helps constrain the timeline of galactic evolution. As Ivanov stated in a UPitt press release:
This galaxy was developing bars 2 billion years after the birth of the Universe. Two billion years after the Big Bang. It's the highest redshift, spectroscopically confirmed, unlensed barred spiral galaxy. In principle, I think that this is not an epoch in which you expect to find many of these objects. It helps to constrain the timescales of bar formation. And it’s just really interesting.
The original version of this article was published on Universe Today.
 Matthew WilliamsScience journalist
Matthew WilliamsScience journalistMatt Williams is a science communicator, journalist, writer, and educator with over 20 years of experience in education and outreach. His articles have appeared in Universe Today, Interesting Engineering, HeroX, Phys.org, Business Insider, Popular Mechanics, and other notable publications. He is the host of Stories from Space, a weekly podcast about the past, present, and future of spaceflight, and a science fiction author with multiple published titles.
Show More CommentsYou must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
Logout Read more James Webb telescope may have discovered the earliest, most distant black hole ever seen
James Webb telescope may have discovered the earliest, most distant black hole ever seen
 James Webb telescope may have spotted the earliest supernova in the universe
James Webb telescope may have spotted the earliest supernova in the universe
 'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
 'Not so exotic anymore': The James Webb telescope is unraveling the truth about the universe's first black holes
'Not so exotic anymore': The James Webb telescope is unraveling the truth about the universe's first black holes
 First Vera Rubin Observatory image reveals hidden structure as long as the Milky Way trailing behind a nearby galaxy — Space photo of the week
First Vera Rubin Observatory image reveals hidden structure as long as the Milky Way trailing behind a nearby galaxy — Space photo of the week
 Giant rotating string of galaxies is 'probably the largest spinning object' in the known universe
Latest in Astronomy
Giant rotating string of galaxies is 'probably the largest spinning object' in the known universe
Latest in Astronomy
 James Webb telescope reveals sharpest-ever look at the edge of a supermassive black hole
James Webb telescope reveals sharpest-ever look at the edge of a supermassive black hole
 Strange discovery offers 'missing link' in planet formation
Strange discovery offers 'missing link' in planet formation
 James Webb telescope spots 'failed stars' in a breathtaking cluster near Earth — Space photo of the week
James Webb telescope spots 'failed stars' in a breathtaking cluster near Earth — Space photo of the week
 NASA's Mars Sample Return is dead, leaving China to retrieve signs of life from the Red Planet
NASA's Mars Sample Return is dead, leaving China to retrieve signs of life from the Red Planet
 James Webb telescope saw black holes emerging from 'cocoons' near the dawn of time
James Webb telescope saw black holes emerging from 'cocoons' near the dawn of time
 'One of those rare 'wow' moments': Zombie star near Earth has a rainbow shockwave that 'shouldn't be there'
Latest in News
'One of those rare 'wow' moments': Zombie star near Earth has a rainbow shockwave that 'shouldn't be there'
Latest in News
 Ever seen a pet cow pick up a broom and scratch herself with it? You have now
Ever seen a pet cow pick up a broom and scratch herself with it? You have now
 Why is flu season so bad this year?
Why is flu season so bad this year?
 Remnants of spills on Renaissance-era textbook reveal recipes for 'curing' ailments with lizard heads and human feces
Remnants of spills on Renaissance-era textbook reveal recipes for 'curing' ailments with lizard heads and human feces
 Romans regularly soaked in filthy, lead-contaminated bath water, Pompeii study finds
Romans regularly soaked in filthy, lead-contaminated bath water, Pompeii study finds
 Watch NASA roll its historic Artemis II moon rocket to the launch pad this weekend
Watch NASA roll its historic Artemis II moon rocket to the launch pad this weekend
 Astronomers confirm earliest Milky Way-like galaxy in the universe, just 2 billion years after the Big Bang
LATEST ARTICLES
Astronomers confirm earliest Milky Way-like galaxy in the universe, just 2 billion years after the Big Bang
LATEST ARTICLES 1Giant underwater plumes triggered by 7-story waves at Nazaré captured off Portuguese coast
1Giant underwater plumes triggered by 7-story waves at Nazaré captured off Portuguese coast- 2Indigenous TikTok star 'Bush Legend' is actually AI-generated, leading to accusations of 'digital blackface'
- 3Ever seen a pet cow pick up a broom and scratch herself with it? You have now
- 4HP Omen Max 16 (2025) review: This heavyweight pushes everything to the max
- 5Eerie 'sand burials' of elite Anglo-Saxons and their 'sacrificed' horse discovered near UK nuclear power plant



